演算法 & 資料結構
#自己的定義
電腦的資料說穿了就只有0和1,怎麼擺放0和1就是資料結構。
怎麼用和算就是演算法。
電腦的資料說穿了就只有0和1,怎麼擺放0和1就是資料結構。
怎麼用和算就是演算法。
電腦要如何完成「排序」(sort) 這件工作呢?「二元樹」 (binary tree) 怎樣子應用在排序這項工作呢?
二元樹是數據結構。 它的關鍵特徵是樹中的每個節點最多可以有兩個子節點,它們按值排列,左邊的子節點值較低,右邊節點較高。
樹狀結構Trees
樹柱結構是一種非線性結構。例如族譜,組織架構。在資料科學方面可以應用到電腦的作業系統和資料庫管理。像我們最常看的排序就是一種運用。
Decision tree
當然機器學習中的決策樹也是一種應用
Binary Tree: Traversal(尋訪)
連結串列Linked list
樹的結構與規範
01. 樹根root
02.節點node
node為n個互斥的集合,n>=0,互斥的集合也是一棵樹稱為子樹
03.不能有重邊
04.不能有迴圈
05.不能不連通
06. 分支度(Degree)
07. 階層(Level)
08. 高度(Height)
09. 終端節點(Terminal Nodes)
10. 父節點(Parent)
11. 子節點(Children)
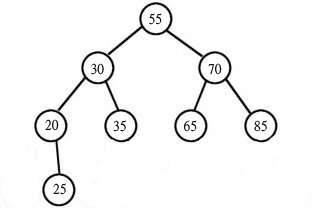
建立一排數列為: 55,70,30,65,20,25,35,85
*中序法依序排列
root=55
70>55,在55右邊
30<55,在55左邊
65>55,在55右邊,但65<70,在70左邊
以此類推
#python二元樹排序
*定義Tree
class Node:
def __init__(self, val):
self.l_child = None
self.r_child = None
self.data = val
def __init__(self, val):
self.l_child = None
self.r_child = None
self.data = val
*插入node
r = Node(55)
binary_insert(r, Node(70))
binary_insert(r, Node(30))
binary_insert(r, Node(65))
binary_insert(r, Node(20))
binary_insert(r, Node(25))
binary_insert(r, Node(35))
binary_insert(r, Node(85))
def binary_insert(root, node):
if root is None:
root = node
else:
if root.data > node.data:
if root.l_child is None:
root.l_child = node
else:
binary_insert(root.l_child, node)
else:
if root.r_child is None:
root.r_child = node
else:
binary_insert(root.r_child, node)
def in_order_print(root):
if not root:
return
in_order_print(root.l_child)
print(root.data)
in_order_print(root.r_child)
def pre_order_print(root):
if not root:
return
print(root.data)
pre_order_print(root.l_child)
pre_order_print(root.r_child)
binary_insert(r, Node(70))
binary_insert(r, Node(30))
binary_insert(r, Node(65))
binary_insert(r, Node(20))
binary_insert(r, Node(25))
binary_insert(r, Node(35))
binary_insert(r, Node(85))
def binary_insert(root, node):
if root is None:
root = node
else:
if root.data > node.data:
if root.l_child is None:
root.l_child = node
else:
binary_insert(root.l_child, node)
else:
if root.r_child is None:
root.r_child = node
else:
binary_insert(root.r_child, node)
def in_order_print(root):
if not root:
return
in_order_print(root.l_child)
print(root.data)
in_order_print(root.r_child)
def pre_order_print(root):
if not root:
return
print(root.data)
pre_order_print(root.l_child)
pre_order_print(root.r_child)
in_order_print(r)